728x90
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define WAIT 60
static const char* flag = "[REDACTED]";
static char data[10][100];
static int input_lengths[10];
static int inputs = 0;
int tgetinput(char *input, unsigned int l)
{
fd_set input_set;
struct timeval timeout;
int ready_for_reading = 0;
int read_bytes = 0;
if( l <= 0 )
{
printf("'l' for tgetinput must be greater than 0\n");
return -2;
}
/* Empty the FD Set */
FD_ZERO(&input_set );
/* Listen to the input descriptor */
FD_SET(STDIN_FILENO, &input_set);
/* Waiting for some seconds */
timeout.tv_sec = WAIT; // WAIT seconds
timeout.tv_usec = 0; // 0 milliseconds
/* Listening for input stream for any activity */
ready_for_reading = select(1, &input_set, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
/* Here, first parameter is number of FDs in the set,
* second is our FD set for reading,
* third is the FD set in which any write activity needs to updated,
* which is not required in this case.
* Fourth is timeout
*/
if (ready_for_reading == -1) {
/* Some error has occured in input */
printf("Unable to read your input\n");
return -1;
}
if (ready_for_reading) {
read_bytes = read(0, input, l-1);
if(input[read_bytes-1]=='\n'){
--read_bytes;
input[read_bytes]='\0';
}
if(read_bytes==0){
printf("No data given.\n");
return -4;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
printf("Timed out waiting for user input. Press Ctrl-C to disconnect\n");
return -3;
}
return 0;
}
static void data_write() {
char input[100];
char len[4];
long length;
int r;
printf("Please enter your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(input, 100);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
while (true) {
printf("Please enter the length of your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(len, 4);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((length = strtol(len, NULL, 10)) == 0) {
puts("Please put in a valid length");
} else {
break;
}
}
if (inputs > 10) {
inputs = 0;
}
strcpy(data[inputs], input);
input_lengths[inputs] = length;
printf("Your entry number is: %d\n", inputs + 1);
inputs++;
}
static void data_read() {
char entry[4];
long entry_number;
char output[100];
int r;
memset(output, '\0', 100);
printf("Please enter the entry number of your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(entry, 4);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((entry_number = strtol(entry, NULL, 10)) == 0) {
puts(flag);
fseek(stdin, 0, SEEK_END);
exit(0);
}
entry_number--;
strncpy(output, data[entry_number], input_lengths[entry_number]);
puts(output);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
char input[3] = {'\0'};
long command;
int r;
puts("Hi, welcome to my echo chamber!");
puts("Type '1' to enter a phrase into our database");
puts("Type '2' to echo a phrase in our database");
puts("Type '3' to exit the program");
while (true) {
r = tgetinput(input, 3);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((command = strtol(input, NULL, 10)) == 0) {
puts("Please put in a valid number");
} else if (command == 1) {
data_write();
puts("Write successful, would you like to do anything else?");
} else if (command == 2) {
if (inputs == 0) {
puts("No data yet");
continue;
}
data_read();
puts("Read successful, would you like to do anything else?");
} else if (command == 3) {
return 0;
} else {
puts("Please type either 1, 2 or 3");
puts("Maybe breaking boundaries elsewhere will be helpful");
}
}
return 0;
}
위와 같은 아주 간단한 코드가 있다.
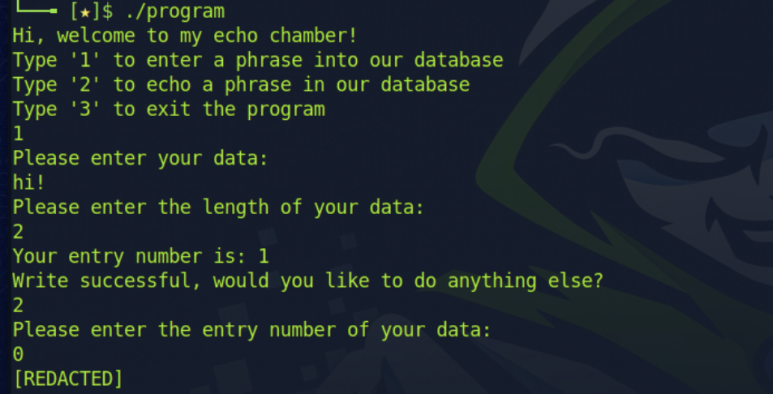
취약점을 이용한 아주 간단한 공격에도 바로 [REDACTED] 즉 중요한 메모리를 반환하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define WAIT 60
#define MAX_INPUT_LENGTH 100
static const char* flag = "[REDACTED]";
static char data[10][MAX_INPUT_LENGTH];
static int input_lengths[10];
static int inputs = 0;
int tgetinput(char *input, unsigned int l)
{
fd_set input_set;
struct timeval timeout;
int ready_for_reading = 0;
int read_bytes = 0;
if( l <= 0 )
{
printf("'l' for tgetinput must be greater than 0\n");
return -2;
}
/* Empty the FD Set */
FD_ZERO(&input_set );
/* Listen to the input descriptor */
FD_SET(STDIN_FILENO, &input_set);
/* Waiting for some seconds */
timeout.tv_sec = WAIT; // WAIT seconds
timeout.tv_usec = 0; // 0 milliseconds
/* Listening for input stream for any activity */
ready_for_reading = select(1, &input_set, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
/* Here, first parameter is number of FDs in the set,
* second is our FD set for reading,
* third is the FD set in which any write activity needs to updated,
* which is not required in this case.
* Fourth is timeout
*/
if (ready_for_reading == -1) {
/* Some error has occured in input */
printf("Unable to read your input\n");
return -1;
}
if (ready_for_reading) {
read_bytes = read(0, input, l-1);
if(input[read_bytes-1]=='\n'){
--read_bytes;
input[read_bytes]='\0';
}
if(read_bytes==0){
printf("No data given.\n");
return -4;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
printf("Timed out waiting for user input. Press Ctrl-C to disconnect\n");
return -3;
}
return 0;
}
static void data_write() {
char input[MAX_INPUT_LENGTH];
char len[4];
long length;
int r;
printf("Please enter your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(input, MAX_INPUT_LENGTH);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
while (true) {
printf("Please enter the length of your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(len, 4);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((length = strtol(len, NULL, 10)) == 0 || length >= MAX_INPUT_LENGTH) {
puts("Please put in a valid length");
} else {
break;
}
}
if (inputs > 10) {
inputs = 0;
}
strncpy(data[inputs], input, length);
data[inputs][length] = '\0'; // Ensure null termination
input_lengths[inputs] = length;
printf("Your entry number is: %d\n", inputs + 1);
inputs++;
}
static void data_read() {
char entry[4];
long entry_number;
char output[100];
int r;
memset(output, '\0', 100);
printf("Please enter the entry number of your data:\n");
r = tgetinput(entry, 4);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((entry_number = strtol(entry, NULL, 10)) == 0 || entry_number > inputs || entry_number < 1) {
puts("Please put in a valid entry number");
return;
}
entry_number--;
strncpy(output, data[entry_number], input_lengths[entry_number]);
output[input_lengths[entry_number]] = '\0'; // Ensure null termination
puts(output);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
char input[3] = {'\0'};
long command;
int r;
puts("Hi, welcome to my echo chamber!");
puts("Type '1' to enter a phrase into our database");
puts("Type '2' to echo a phrase in our database");
puts("Type '3' to exit the program");
while (true) {
r = tgetinput(input, 3);
// Timeout on user input
if(r == -3)
{
printf("Goodbye!\n");
exit(0);
}
if ((command = strtol(input, NULL, 10)) == 0) {
puts("Please put in a valid number");
} else if (command == 1) {
data_write();
puts("Write successful, would you like to do anything else?");
} else if (command == 2) {
if (inputs == 0) {
puts("No data yet");
continue;
}
data_read();
puts("Read successful, would you like to do anything else?");
} else if (command == 3) {
return 0;
} else {
puts("Please type either 1, 2 or 3");
puts("Maybe breaking boundaries elsewhere will be helpful");
}
}
return 0;
}
코드를 패치한다
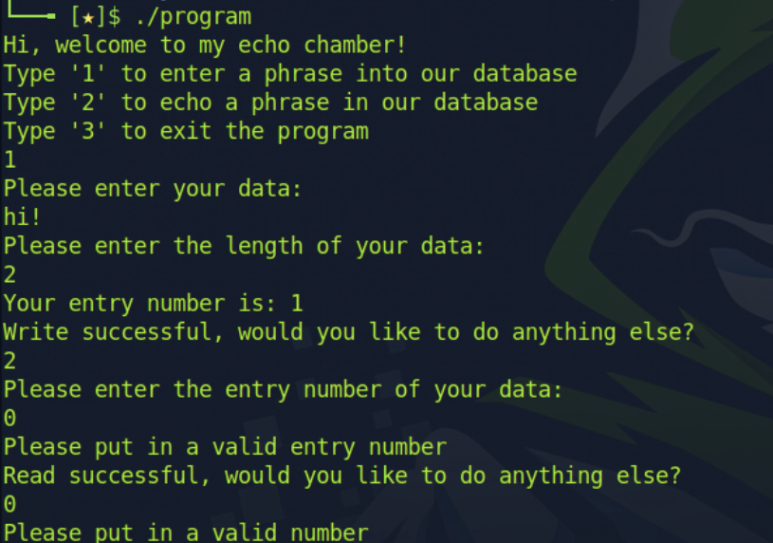
기존 코드가 가지고 있던 두 가지 취약점이 모두 패치되어 기존의 공격은 뚫리지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
728x90
'호그와트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 흠냐 (0) | 2023.06.29 |
|---|---|
| gpt도 활용하는 방법이 있어요 그냥 무턱대고 쓰는게 절대로 아니랍니당~ (헤헷 4 의 위력) (1) | 2023.06.28 |
| 주식 주식 바운스~ 바운스~ (0) | 2023.06.20 |
| rot13 (0) | 2023.06.20 |
| 퓨어 알티지 DHA 오메가 3 (0) | 2023.06.18 |